|
Minireviews |
A review on computational models for predicting protein solubility
|
| Teerapat Pimtawong, Jun Ren, Jingyu Lee, Hyang-Mi Lee, Dokyun Na |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2408001
|
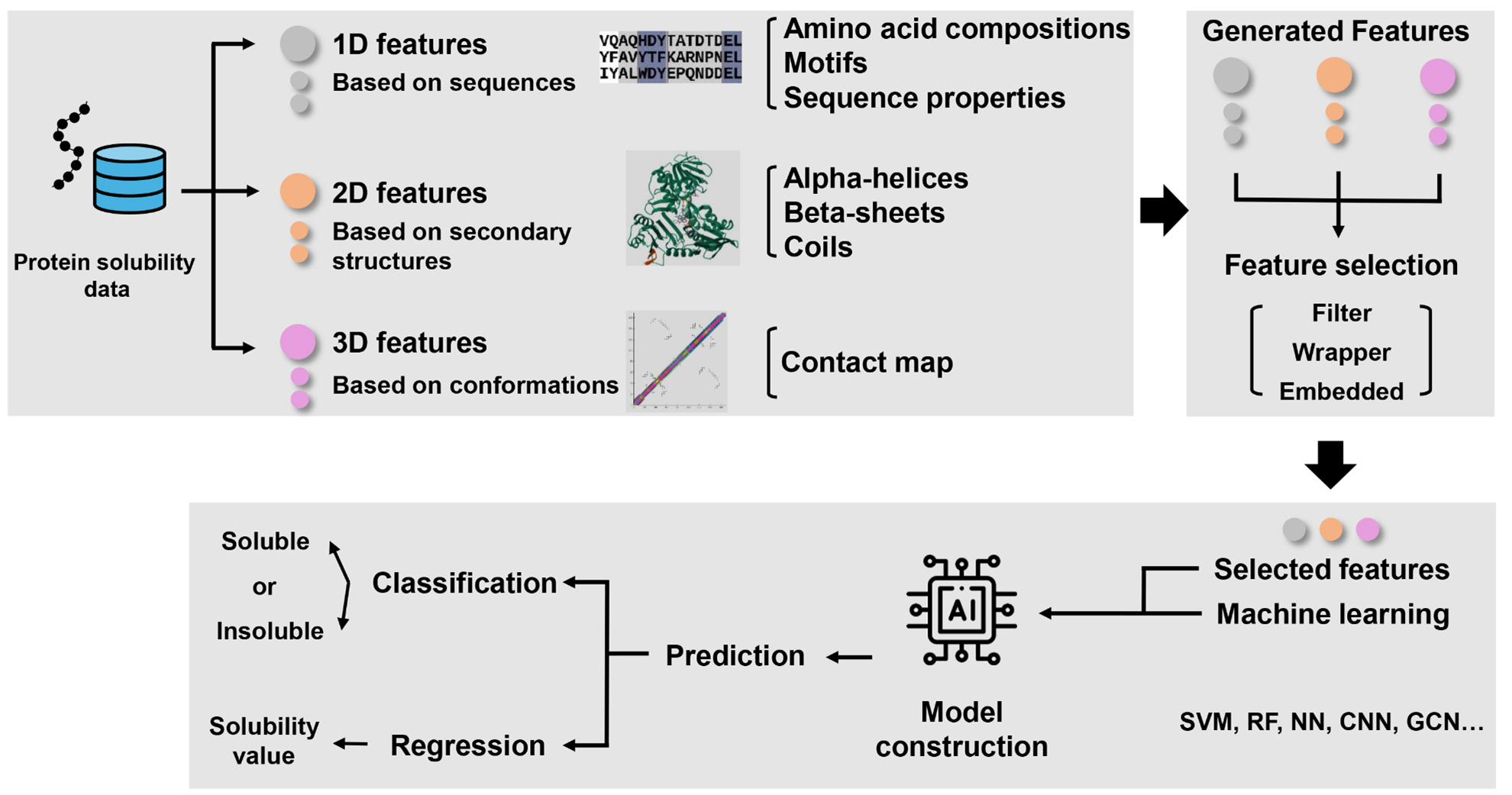 |
Protein solubility is a critical factor in the production of recombinant proteins, which are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and biotechnology. Predicting protein solubility remains a challenging task due to the complexity of protein structures and the multitude of factors influencing solubility. Recent advances in computational methods, particularly those based on machine learning, have provided powerful tools... |
|
|
|
|
|
Advances in functional analysis of the microbiome: Integrating metabolic modeling, metabolite prediction, and pathway inference with Next-Generation Sequencing data
|
| Sungwon Jung |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2411006
|
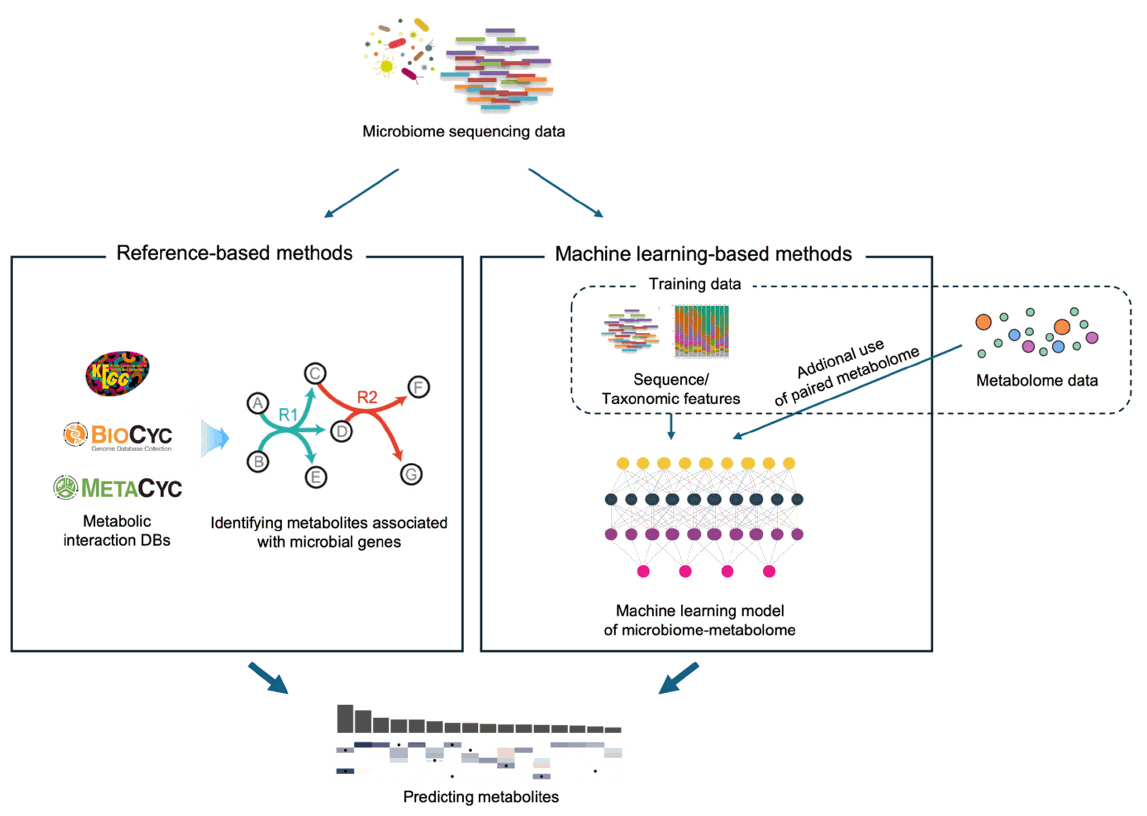 |
This review explores current advancements in microbiome functional analysis enabled by next-generation sequencing technologies, which have transformed our understanding of microbial communities from mere taxonomic composition to their functional potential. We examine approaches that move beyond species identification to characterize microbial activities, interactions, and their roles in host health and disease. Genome-scale metabolic models allow for in-depth simulations of metabolic... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Full articles |
Virgibacillus saliphilus sp. nov. and Virgibacillus salidurans sp. nov., isolated from kimchi
|
| Young Joon Oh, Joon Yong Kim, Min-Sung Kwon, Sulhee Lee, Sang-Pil Choi, Hak-Jong Choi |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2501001
|
|
This study aimed to provide a taxonomic description of two bacterial strains, NKC19-3T and NKC19-16T, isolated from commercially produced kimchi obtained from various regions within the Republic of Korea. Both strains were rod-shaped, gram-stain-positive, facultatively anaerobic, and displayed positive reactions for oxidase and catalase. Additionally, these bacteria were motile, halophilic (salt-tolerant), and proliferated under alkaline conditions. Genetically, both strains showed 98.0% similarity in their 16S rRNA gene sequences and were most closely related to Virgibacillus natechei FarDT, with 96.5 and 96.8% sequence similarity, respectively. ANI values indicated that the two novel strains were distinct from V. natechei FarDT, as they were below the species demarcation threshold. The ANI value between strains NKC19-3ᵀ and NKC19-16ᵀ was 84.64–84.75%, and the values between these strains and other related strains did not exceed 80.0%, further supporting their classification as novel species. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that strains NKC19-3T and NKC19-16T formed a distinct branch within the genus Virgibacillus, clearly distinguishing them from other species in the same genus. Regarding genomic characteristics, the GC content was 38.9% for strain NKC19-3T and 39.5% for strain NKC19-16T. The genome of strain NKC19-3T had a size of approximately 4.1 Mb and contained 3,785 protein-coding genes (CDSs). Strain NKC19-16T had a slightly smaller genome, approximately 3.9 Mb in size and harbored 3,726 CDSs. The polar lipid profiles of strains NKC19-3ᵀ and NKC19-16ᵀ included diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), glycolipids (GL), and an unidentified lipid (L). The predominant fatty acids of both strains were anteiso-C15:0 and anteiso-C17:0. Considering the comprehensive analysis encompassing phenotypic, genomic, phylogenetic, and chemotaxonomic data, strains NKC19-3T and NKC19-16T are proposed to represent two novel species within the genus Virgibacillus. The suggested names for these species are Virgibacillus saliphilus sp. nov. (type strain NKC19-3T, also referred to as KACC 22326T and DSM 112707T) and Virgibacillus salidurans sp. nov. (type strain NKC19-16T, also referred to as KACC 22327T and DSM 112708T). |
|
|
|
|
|
PneusPage: A WEB-BASED TOOL for the analysis of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data of Streptococcus pneumonia
|
| Eunju Hong, Youngjin Shin, Hyunseong Kim, Woo Young Cho, Woo-Hyun Song, Seung-Hyun Jung, Minho Lee |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409020
|
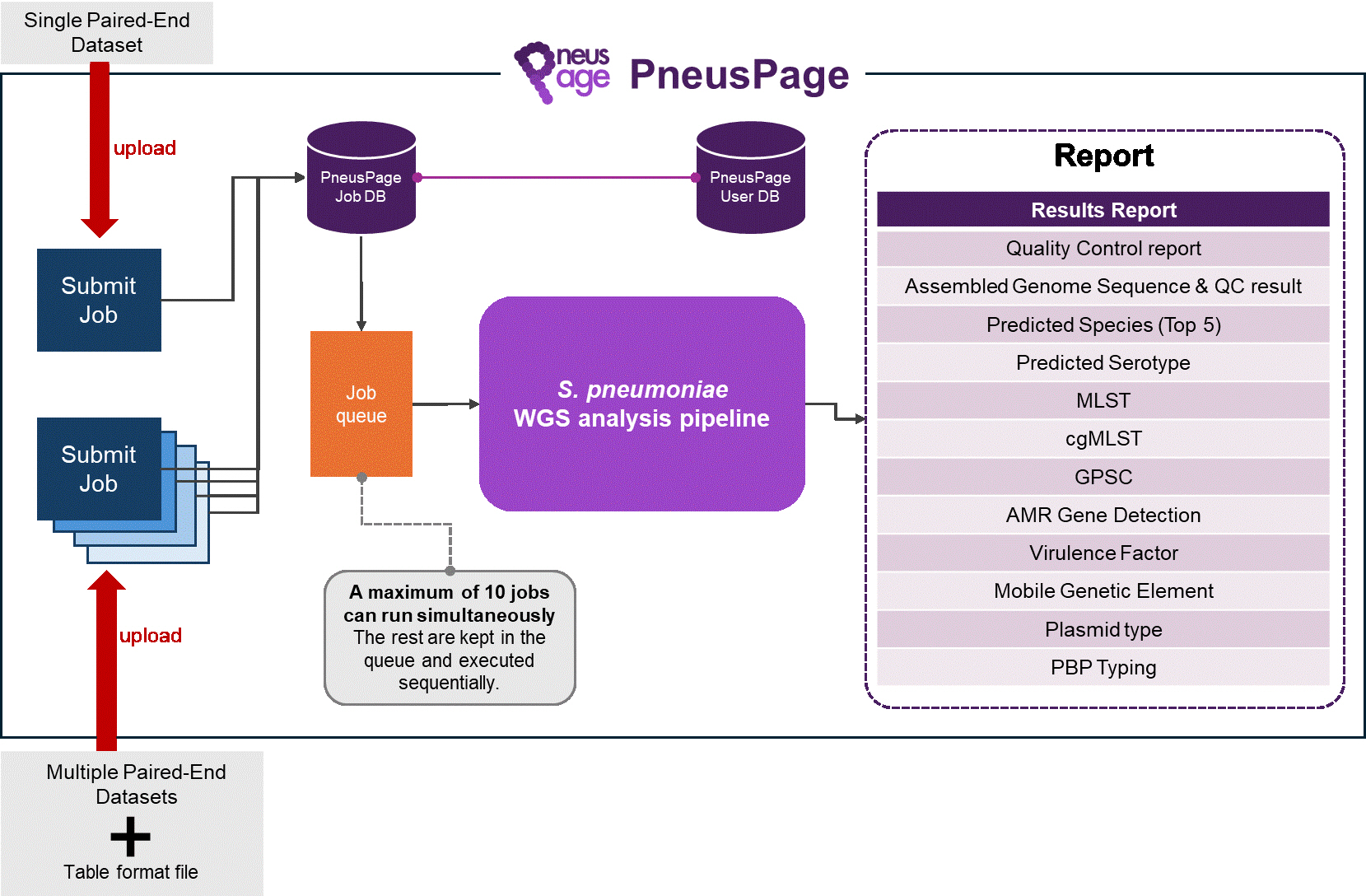 |
With the advent of whole-genome sequencing, opportunities to investigate the population structure, transmission patterns, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and virulence determinants of Streptococcus pneumoniae at high resolution have been increasingly expanding. Consequently, a user-friendly bioinformatics tool is needed to automate the analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae whole-genome sequencing data, summarize clinically relevant genomic features, and further guide treatment options. Here, we developed... |
|
|
|
|
|
Simultaneous gene editing of both nuclei in a dikaryotic strain of Ganoderma lucidum using Cas9-gRNA ribonucleoprotein
|
| Yeon-Jae Choi, Hyerang Eom, Rutuja Nandre, Minseek Kim, Youn-Lee Oh, Sinil Kim, Hyeon-Su Ro |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409006
|
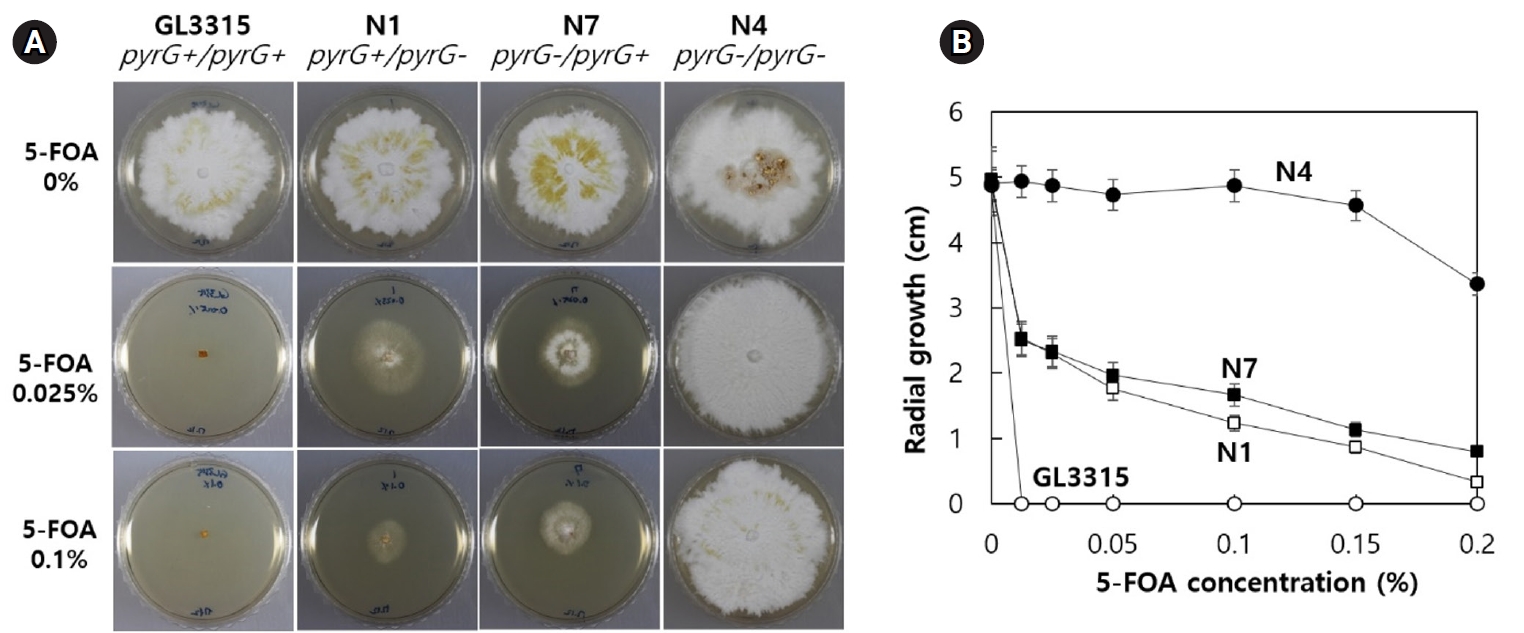 |
The presence of multiple nuclei in a common cytoplasm poses a significant challenge to genetic modification in mushrooms. Here, we demonstrate successful gene editing in both nuclei of a dikaryotic strain of Ganoderma lucidum using the Cas9-gRNA ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP). The RNP targeting the pyrG gene was introduced into dikaryotic protoplasts of G. lucidum, resulting in the isolation of 31... |
|
|
|
|
|
Lactic acid bacteria from Ethiopian traditional beverage, Tella: technological and metabolic profiles for industrial application
|
| Gashaw Assefa Yehuala, Jaein Choe, Nurelegne Tefera Shibeshi, Kumsa Delessa, Asnake Desalegn, Mi-Kyung Park |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409008
|
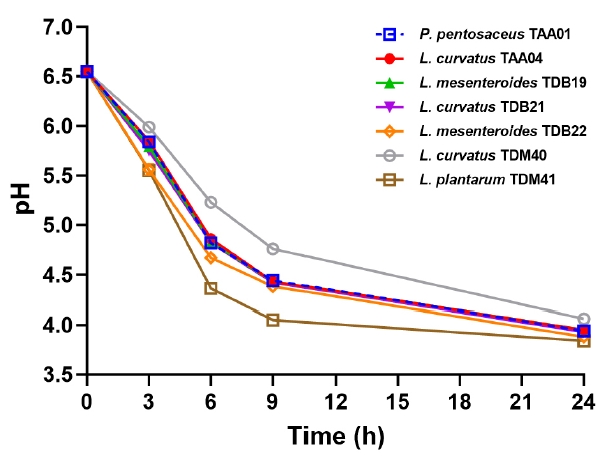 |
Tella is a traditional beverage widely accepted by consumers, despite the lack of product consistency owing to its reliance on natural fermentation. This study aimed to identify potential industrial lactic acid bacteria (LAB) starter cultures based on their technological properties. Seven LAB strains isolated from Tella were characterized for their carbohydrate utilization, salt content, temperature, and acid tolerances, growth and... |
|
|
|
|
|
Korean Red ginseng enhances ZBP1-mediated cell death to suppress viral protein expression in host defense against Influenza A virus
|
| Jueun Oh, Hayeon Kim, Jihye Lee, Suhyun Kim, Seyun Shin, Young-Eui Kim, Sehee Park, SangJoon Lee |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409007
|
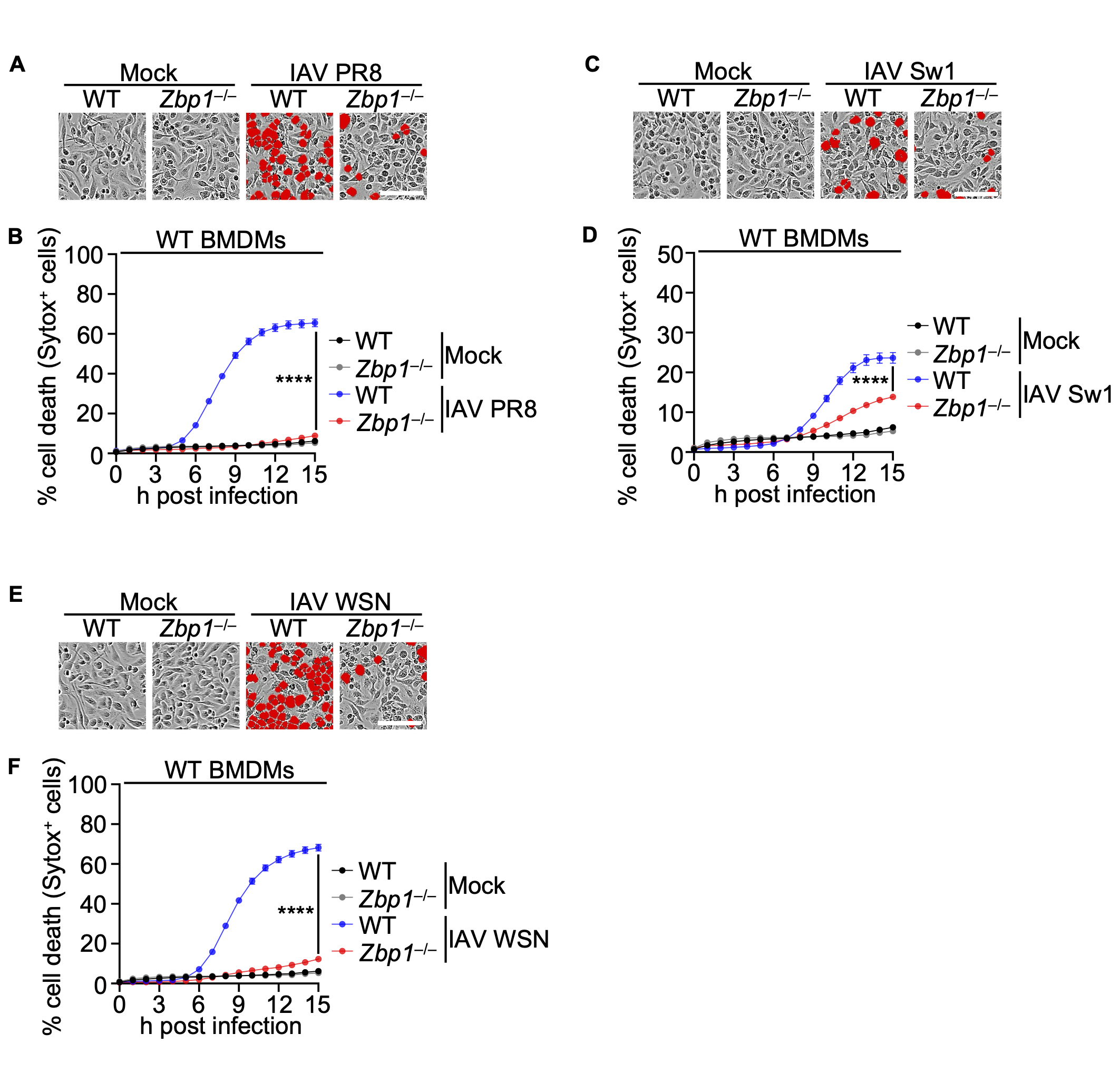 |
Korean Red ginseng has emerged as a potent candidate in the fight against various viral infections, demonstrating significant efficacy both in vitro and in vivo, particularly against influenza A viruses. Despite substantial evidence of its antiviral properties, the detailed molecular mechanisms through which it reduces viral lethality remain insufficiently understood. Our investigations have highlighted the superior effectiveness of Korean Red... |
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of skin microbiome associated with disease severity in systemic sclerosis
|
| Kyung-Ann Lee, Asad Ul-Haq, Hoonhee Seo, Sujin Jo, Sukyung Kim, Ho-Yeon Song, Hyun-Sook Kim |
|
DOI: http://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409018
|
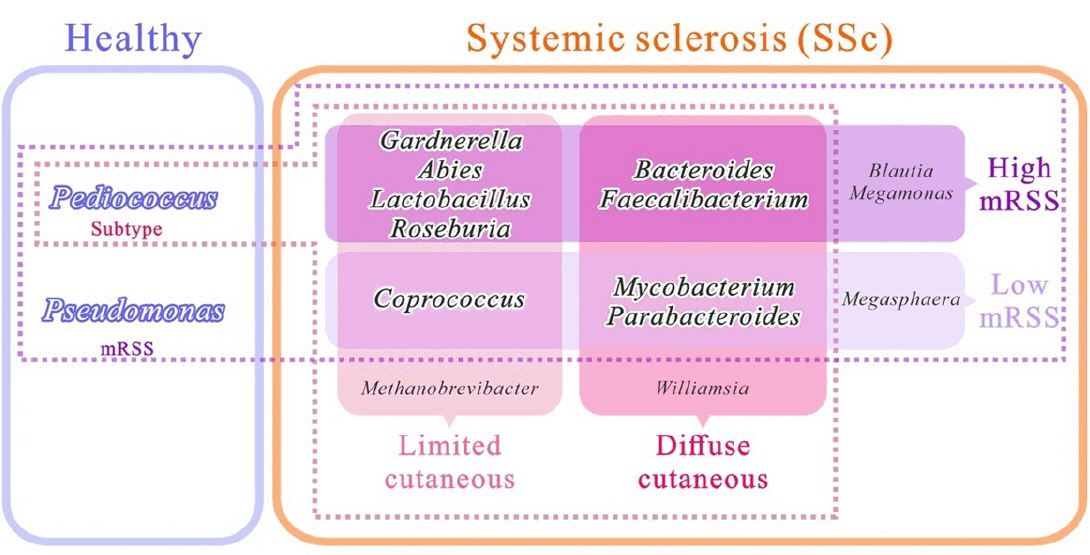 |
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterised by skin fibrosis and internal organ involvement. Disruptions in the microbial communities on the skin may contribute to the onset of autoimmune diseases that affect the skin. However, current research on the skin microbiome in SSc is lacking. This study aimed to investigate skin microbiome associated with disease severity in SSc.... |
|
|
|
|
|







